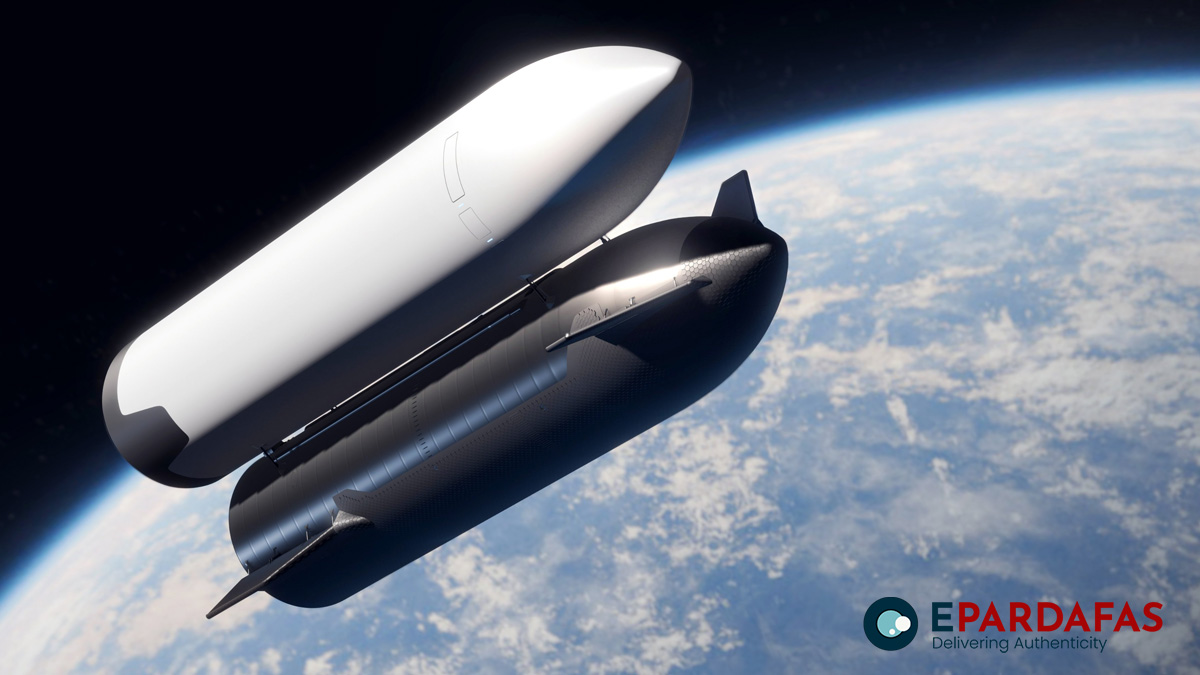
In a landmark event, SpaceX successfully launched two robotic lunar landers developed by the United States and Japan to the Moon on a single Falcon 9 rocket early Wednesday. The Blue Ghost lander, developed by Firefly Aerospace, and the Resilience lander, created by Japanese company ispace, were launched at 1:13 a.m. Eastern Time from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mission marked another milestone for SpaceX, with the Falcon 9’s first stage returning safely to a droneship stationed in the Atlantic Ocean.
The Blue Ghost lander is on a 45-day journey to the Moon, targeting a landing near Mons Latreille in Mare Crisium, a volcanic basin on the Moon’s near side. It carries 10 scientific investigations as part of NASA’s Moon to Mars initiative. These experiments aim to enhance understanding of the lunar environment and support future human missions, focusing on areas like lunar subsurface drilling, regolith sampling, and the mitigation of lunar dust. NASA has emphasized the potential benefits of these findings for Earth, particularly in understanding how space weather and cosmic forces impact the planet.
The Resilience lander, developed by ispace, has embarked on a four-to-five-month voyage to the Moon. Its mission involves achieving a soft landing, deploying the TENACIOUS Micro Rover, exploring the lunar surface, and collecting regolith samples. This mission reflects growing international collaboration in space exploration, with both landers set to contribute significantly to advancing scientific knowledge and preparing for future lunar missions.













Comments